In today’s digital age, businesses and consumers are increasingly demanding faster, more efficient ways to process and analyze data. While traditional cloud computing has served as the backbone for modern IT infrastructures, another computing paradigm is gaining momentum: Edge Computing.
But what exactly is edge computing, and why is it becoming so crucial for certain industries? In this blog, we’ll explore the concept of edge computing, how it differs from cloud computing, and which sectors stand to benefit most from its implementation.
What is Edge Computing?
At its core, Edge Computing refers to a distributed computing model where data processing and analysis happen closer to the source of data, rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers. The term “edge” refers to the outermost part of a network, closer to where devices or sensors generate data.
In simpler terms, edge computing allows for data to be processed on the “edge” of the network—near the devices or sensors that produce it—before being sent to the cloud or a centralized data center. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enabling faster decision-making and enhanced performance.
How Edge Computing Differs from Cloud Computing
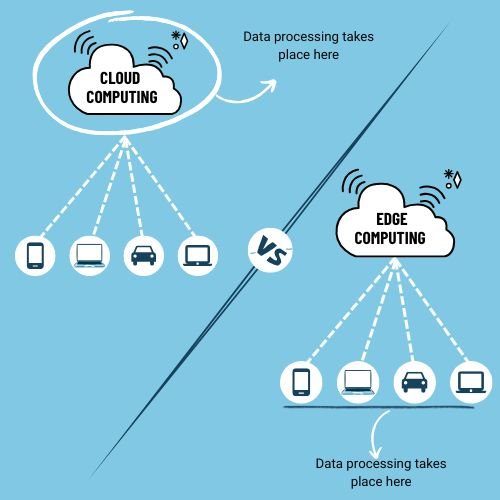
Cloud computing relies on remote servers to process and store data, which are typically located far from the user or device generating the data. While cloud computing offers powerful processing capabilities, it can experience delays due to long-distance data transmission, especially in real-time applications.
Edge computing, on the other hand, decentralizes the processing by moving it closer to the data source. This results in several advantages:
Lower Latency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the time it takes for data to travel to a cloud server and back.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Edge computing reduces the need to send massive amounts of data to the cloud for processing, which can save on bandwidth costs and network congestion.
Improved Security: Data processed on-site or at the edge can be more secure because it is not transmitted over long distances, reducing the risk of data interception.
Why is Edge Computing Important?
As the number of connected devices continues to increase, there is an overwhelming amount of data being generated. Many of these devices—such as IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, or sensors—require real-time processing to make quick decisions. Edge computing provides a solution by enabling immediate data analysis and reducing reliance on distant cloud data centers.
In addition, edge computing is essential for applications where high latency or network disruptions could result in failures or safety concerns. For example, industrial robots, healthcare monitoring devices, or smart cities rely on edge computing to ensure continuous, real-time operation.
Who Needs Edge Computing the Most?
While edge computing can benefit a wide range of industries, some sectors are especially well-suited to harness its potential. Let’s take a look at who needs edge computing the most:
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
In manufacturing, edge computing is crucial for real-time process monitoring, predictive maintenance, and machine-to-machine communication. It allows machines and devices to communicate directly with each other, improving operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Healthcare
Healthcare devices such as wearable sensors, medical equipment, and remote monitoring tools generate large volumes of data. Edge computing allows this data to be processed instantly, enabling immediate decision-making for critical conditions. It also helps ensure data privacy by reducing the need to send sensitive information to the cloud.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely heavily on real-time data to make split-second decisions. Edge computing allows vehicles to process sensor data locally and react without the delays associated with cloud computing. This reduces the risk of accidents and improves the safety of autonomous systems.
Smart Cities
In smart cities, edge computing helps with traffic management, waste monitoring, and public safety systems. By processing data from sensors in real-time, cities can improve services, reduce energy consumption, and respond quickly to emergencies.
Retail and Customer Experience
Retailers can use edge computing to enhance in-store experiences by processing customer data locally to provide real-time offers or personalized experiences. It can also be used to track inventory, optimize supply chains, and reduce response times for online orders.
Telecommunications
Telecom providers are increasingly adopting edge computing to improve network performance and reduce latency. By placing data processing at the edge of the network, telecom companies can ensure faster, more reliable services for their customers, particularly in high-demand environments like 5G networks.
Entertainment and Gaming
With the rise of cloud gaming and streaming services, edge computing is becoming critical to deliver high-quality experiences. By reducing latency and ensuring content is delivered close to the user, gaming and streaming platforms can provide smoother, more responsive interactions.
The Future of Edge Computing
As technology evolves, the role of edge computing will only grow. With the proliferation of IoT devices, the rollout of 5G networks, and advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), edge computing will play a pivotal role in powering smart systems across industries.
The convergence of these technologies is making edge computing a cornerstone for the next generation of connected devices. Businesses that implement edge computing solutions today will have a competitive edge in terms of speed, security, and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a transformative technology that brings computing power closer to where data is generated. With its ability to reduce latency, optimize bandwidth usage, and enhance security, edge computing is a critical solution for industries that require real-time data processing and decision-making. As more devices become connected and the demand for faster services increases, edge computing will continue to shape the future of technology and business operations.
Whether you’re in manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, or retail, edge computing offers solutions that can help you streamline processes, improve efficiency, and deliver superior experiences to your customers.
