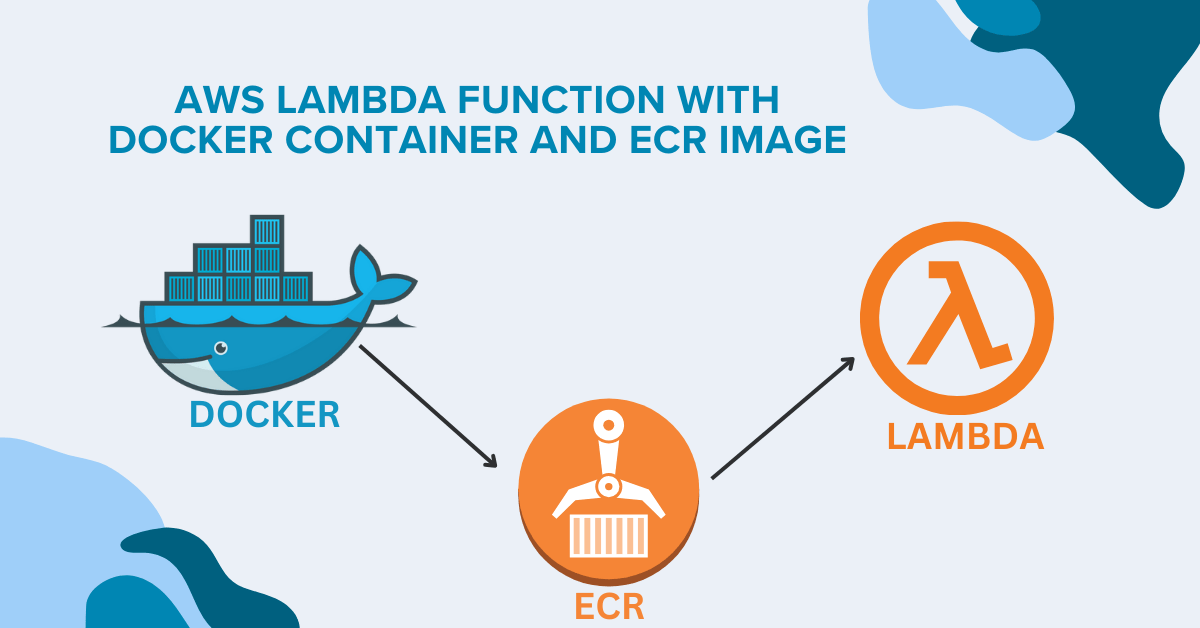
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, efficiency and simplicity are more than just buzzwords—they are the cornerstones of successful digital strategies. AWS Lambda, with its serverless architecture, has become a pivotal service for developers looking to deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. However, as applications grow more complex, so too does the need for streamlined processes. Enter Docker containers and Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)—tools that promise to simplify and supercharge your AWS Lambda functions. This article explores how these technologies work together to make AWS Lambda more accessible, efficient, and powerful.
In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the world of AWS Lambda functions with Docker containers and ECR images. We’ll guide you through every step of the process, from understanding the basics to implementing best practices. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting out with serverless architecture, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to leverage these technologies effectively. Let’s embark on this exciting journey to streamline your serverless deployments!
Understanding AWS Lambda and Docker
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. It automatically scales your applications in response to incoming requests, making it an efficient and cost-effective solution for various use cases, including:
Data processing
Real-time file processing
Web applications
IoT backends
Introduction to Docker containers
Docker is a platform that enables developers to package applications and their dependencies into lightweight, portable containers. These containers can run consistently across different environments, offering several advantages:
Isolation
Portability
Efficiency
Scalability
Benefits of combining Lambda and Docker
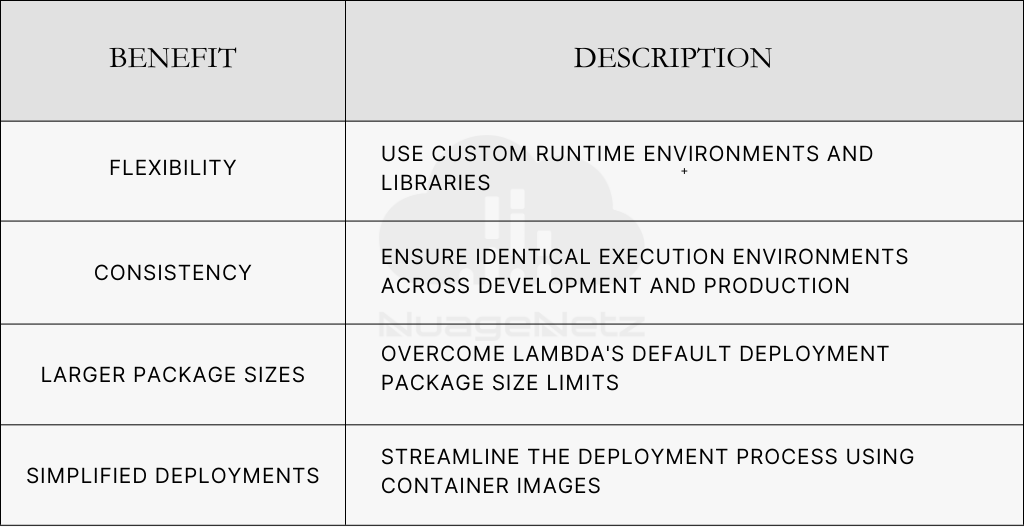
Key advantages of this combination include:
- Custom runtimes: Deploy applications using languages not natively supported by Lambda.
- Dependency management: Package all required libraries and dependencies within the container.
- Local testing: Test Lambda functions locally using Docker before deployment.
- Improved collaboration: Share consistent development environments across teams.
By leveraging Docker containers with AWS Lambda, developers can create more complex and robust serverless applications while maintaining the benefits of both technologies. This approach opens up new possibilities for serverless architecture and application design.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before we dive into creating and deploying AWS Lambda functions with Docker containers, it’s crucial to set up your development environment properly. This step will ensure a smooth workflow as you progress through the process.
A. Installing necessary tools
To get started, you’ll need to install the following essential tools:
- AWS CLI
- Docker
- Python (if not already installed)
- Git (optional, but recommended)
B. Configuring AWS CLI
Once you’ve installed the AWS CLI, you need to configure it with your AWS credentials:
- Open a terminal or command prompt
- Run
aws configure - Enter your AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key
- Specify your default region and output format
C. Creating an AWS ECR repository
To store your Docker images, you’ll need an Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) repository:
- Open the AWS Management Console
- Navigate to the ECR service
- Click “Create repository”
- Name your repository and configure settings as needed
- Note the repository URI for later use
D. Preparing your Docker environment
Ensure your Docker environment is ready:
- Verify Docker installation:
docker --version - Create a new directory for your project
- Initialize a new Dockerfile in this directory
With your development environment set up, you’re now ready to create a Docker container for your Lambda function. In the next section, we’ll explore the process of building a Docker image tailored for AWS Lambda.
Creating a Docker Container for Lambda
Now that we’ve set up our development environment, let’s dive into creating a Docker container for our AWS Lambda function. This process involves three key steps: writing a Dockerfile, building the Docker image, and testing the container locally.
A. Writing a Dockerfile
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.9
# Copy function code
COPY app.py ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT}
# Set the command for Lambda to run your function
CMD [“app.handler”]
This Dockerfile:
- Uses the official AWS Lambda Python 3.9 base image
- Copies our
app.pyfile into the container - Sets the CMD to run our handler function
You can replace app.py with your actual Lambda function code and change the runtime to suit your requirements.
B. Building the Docker image
docker build -t my-lambda-function .
This command:
- Uses
docker buildto create an image - Tags the image with the name
my-lambda-function - Builds the image based on the Dockerfile in the current directory (
.)
C. Testing the container locally
docker run -p 9000:8080 my-lambda-function
curl -XPOST “http://localhost:9000/2015-03-31/functions/function/invocations” -d ‘{}’
Pushing the Docker Image to Amazon ECR
A. Authenticating with ECR
Before pushing our image, we need to authenticate with ECR. Here’s how to do it:
aws ecr get-login-password –region <your-region> | docker login –username AWS –password-stdin <your-account-id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com
<your-region> and <your-account-id> with your specific details. B. Create an ECR Repository
aws ecr create-repository –repository-name hello-world –image-scanning-configuration scanOnPush=true –image-tag-mutability MUTABLE
C. Tagging the Docker image
docker tag your-image-name:tag <your-account-id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com/your-repository-name:tag
D. Pushing the image to ECR
docker push <your-account-id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com/your-repository-name:tag
Configuring AWS Lambda Function
Creating a new Lambda function
To create a new Lambda function, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the AWS Lambda console
- Click on “Create function”
- Choose “Container image” as the function type
- Provide a name for your function
- Select the appropriate runtime (e.g., Python 3.8)
Selecting the container image
After creating the function, you’ll need to specify the container image:
- In the “Container image URI” field, enter the URI of your ECR image
- Choose the appropriate image tag (e.g., “latest” or a specific version)
Configuring execution role and permissions
Ensure your Lambda function has the correct permissions:
- Create or select an IAM role for your function
- Attach policies that grant access to required AWS services (e.g., S3, DynamoDB)
- Review and adjust the execution role’s trust relationship if needed
Testing and Deploying the Lambda Function
{
“statusCode”: 200,
“body”: “Hello from Lambda running in Docker!”
}
Benefits of Using AWS Lambda with Docker Containers
- Greater flexibility: You can customize your function environment beyond what Lambda offers by default.
- Easier development process: Standardized Docker workflows and tools (like CI/CD pipelines) can be used.
- Compatibility: Easily migrate existing Docker-based applications to Lambda, enabling hybrid deployment models.
Conclusion
Deploying AWS Lambda functions with Docker containers and ECR images offers a powerful and flexible approach to serverless computing. By leveraging Docker’s portability and ECR’s secure image storage, developers can create more complex and customizable Lambda functions that meet their specific needs.
Throughout this process, from setting up the development environment to testing and deploying the function, careful attention to best practices and optimization is crucial. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can harness the full potential of AWS Lambda, Docker, and ECR to build scalable, efficient, and cost-effective serverless applications. Embrace this powerful combination to elevate your serverless architecture and drive innovation in your projects.
About Us
NuageNetz IT Services Pvt. Ltd. is a cutting-edge IT company that specializes in Cloud Computing, Web Development, DevOps and Agile Methodologies. Our team of skilled professionals is dedicated to providing exceptional services to our clients using the latest technologies and tools
Got Something to say about our Blog?
Have something to say? Drop your thoughts, feedback, or questions in the comments below!