In today’s interconnected digital world, the term “cloud computing” has become ubiquitous. Whether you’re storing files on Google Drive, streaming music on Spotify, or collaborating with colleagues on a shared document in Microsoft Office 365, chances are you’re already leveraging the power of cloud computing without even realizing it.

Why Use Cloud Computing?
There are several reasons why cloud computing is a better option for businesses:
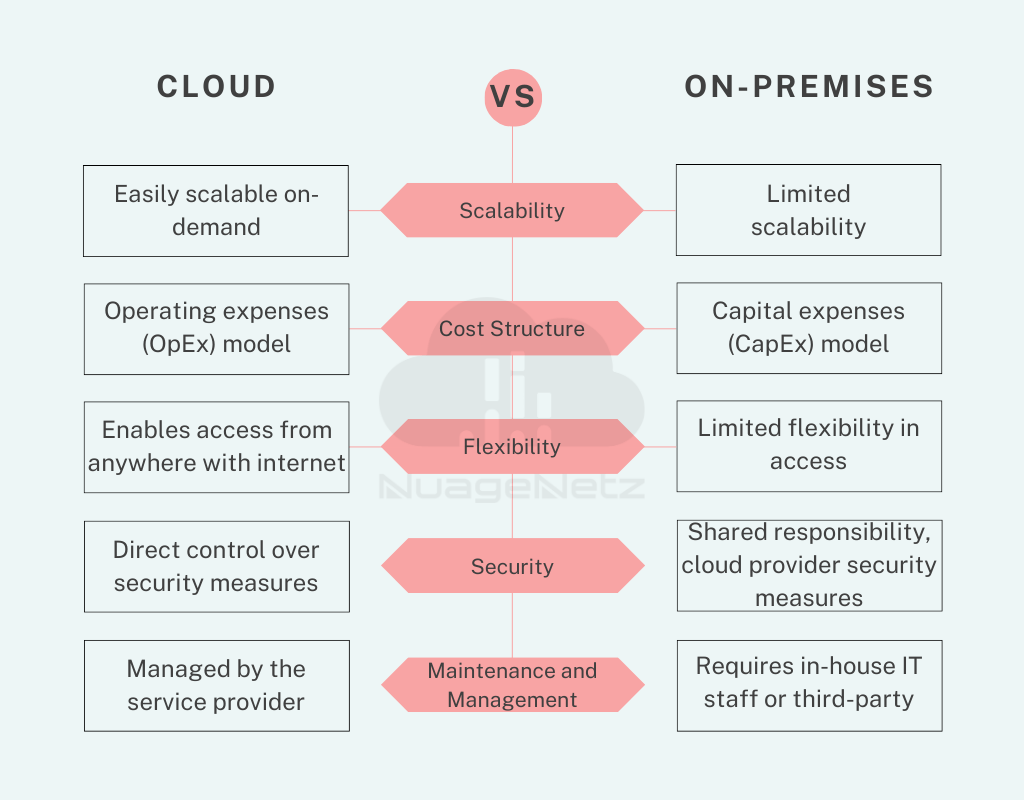
Scalability: Cloud computing allows businesses to easily scale up or down their resources based on demand. This flexibility ensures that the organization always has the appropriate amount of resources to handle heavy traffic or workload.
Cost Efficiency: By outsourcing infrastructure management to cloud service providers, organizations can reduce capital expenditures on hardware and data centers. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go pricing model of many cloud services means users only pay for the resources they consume, optimizing cost efficiency.
Flexibility: With cloud computing, businesses have the flexibility to use and pay for resources as per their needs. They can easily access additional servers, memory elements, and other resources without the need to invest in physical infrastructure.
On-Demand Self-Service: Cloud computing provides businesses with on-demand access to resources and services. Organizations can instantly provision, manage, and control their resources without the need for advanced technical knowledge or assistance.
On-Premises vs. Cloud Computing: Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Types of Cloud Computing:
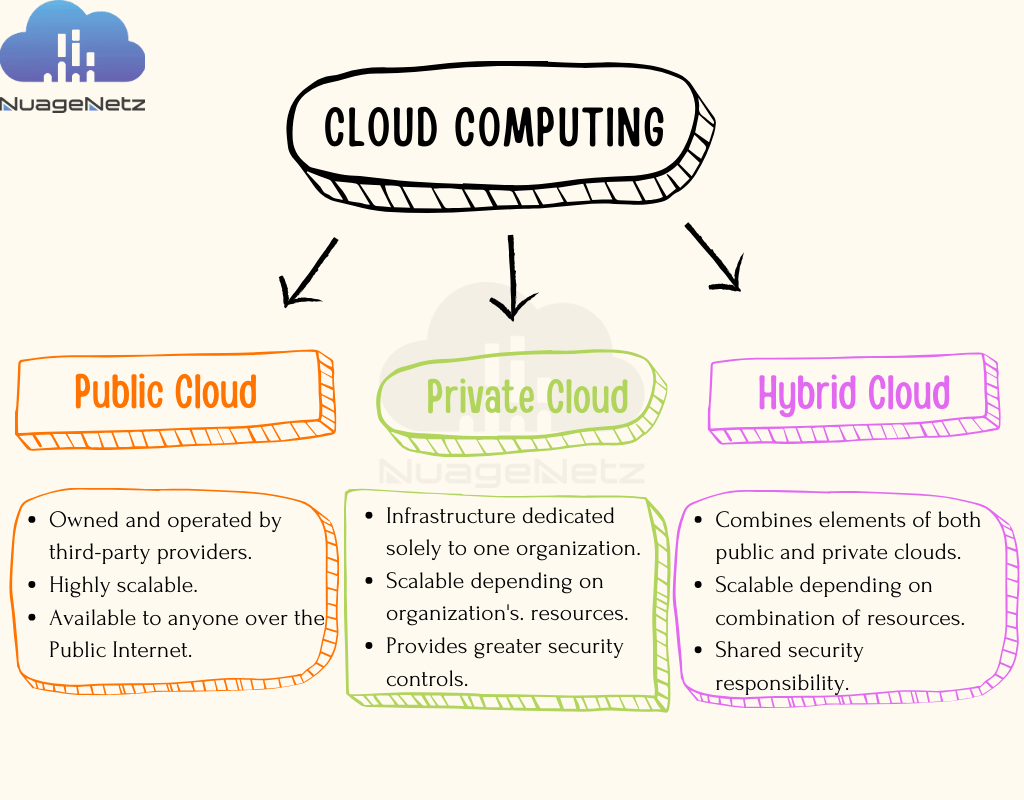
Cloud computing can be categorized based on deployment models and service models.
Deployment Models:
Public Cloud:
Public cloud services are provided by third-party vendors over the internet and are available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them. These services are typically offered on a pay-per-use or subscription basis, and resources are shared among multiple customers. Public clouds offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them popular among startups, small businesses, and enterprises alike.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud.Private Cloud:
Private cloud infrastructure is operated solely for a single organization, whether managed internally or by a third party. It offers greater control, security, and customization compared to public cloud services but requires more upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Private clouds are commonly used by organizations with specific compliance, security, or performance requirements.
Examples: VMware Cloud Foundation, OpenStack, Microsoft Azure Stack.Hybrid Cloud:
Hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. It offers flexibility, allowing organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud while maintaining sensitive data or critical workloads on-premises or in a private cloud environment.
Examples: AWS Outposts, Azure Hybrid, Google Anthos, Red Hat.
Comparison Table: Public, Private and Hybrid Cloud
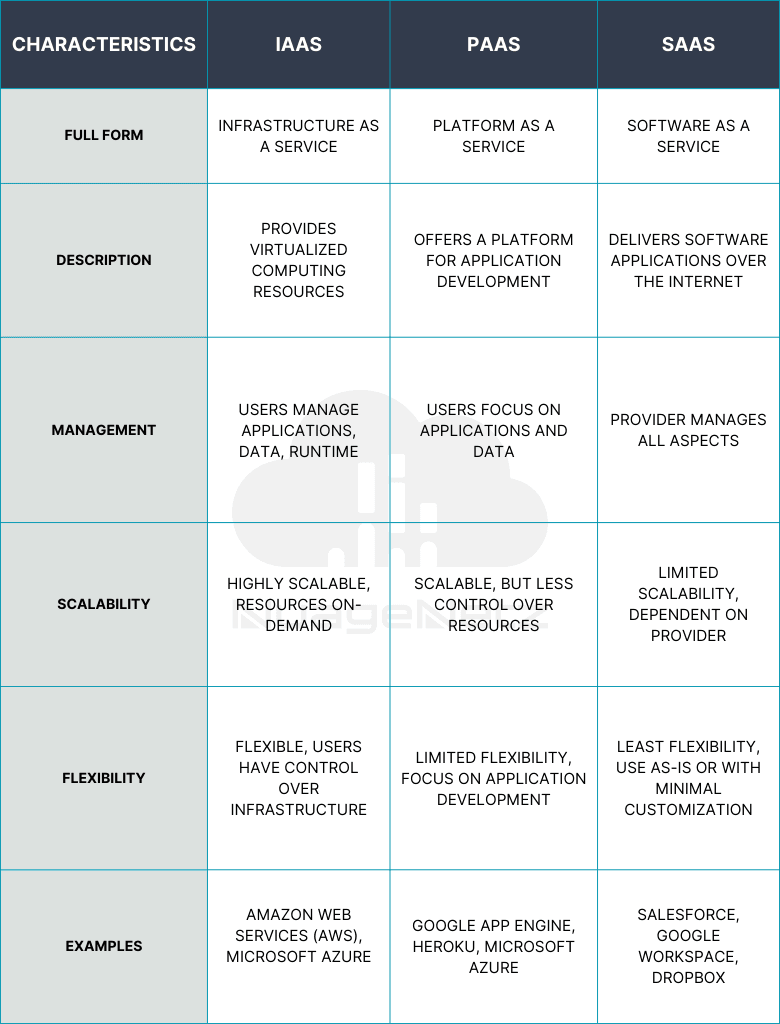
Service Models:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS):
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure from cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis, eliminating the need to invest in physical hardware.
Example providers: Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines, Google Cloud Compute Engine.Platform as a Service (PaaS):
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a platform and environment for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure. PaaS typically includes development tools, middleware, and runtime environments.
Example providers: Heroku, Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine.Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access applications via web browsers, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance.
Example applications: Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365.
Differences between IaaS, PaaS and SaaS:
Exploring the Top Cloud Computing Providers
Cloud service providers offer a wide range of computing services and resources over the internet, empowering organizations to innovate, scale, and optimize their IT operations. Here are some of the leading cloud service providers:
Amazon Web Services (AWS):

Overview: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive and widely-used cloud computing platform provided by Amazon. Launched in 2006, AWS offers a vast array of cloud services, including computing power, storage solutions, networking, databases, machine learning, analytics, security, and more. These services are designed to help businesses and individuals build and deploy applications quickly and securely, without the need to invest in physical infrastructure.
Key Services: Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, AWS Lambda, Amazon Aurora, Amazon Redshift.
Microsoft Azure:

Overview: Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform and services offered by Microsoft. Launched in 2010, Azure provides a wide range of cloud services, including computing power, storage, networking, databases, machine learning, analytics, Internet of Things (IoT), and more. It enables businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications and services through Microsoft’s global network of data centers.
Key Services: Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Blob Storage, Azure SQL Database, Azure Functions, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Azure AI services.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):

Overview: Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services provided by Google, offering a wide range of infrastructure and platform services for computing, storage, networking, machine learning, big data, and more. Launched in 2008, GCP provides businesses with cloud-based solutions to build and scale applications, analyze data, and innovate more rapidly.
Key Services: Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Storage, Google BigQuery, Google Cloud Functions, Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Google AI Platform.
IBM Cloud:

Overview: IBM Cloud offers a range of cloud computing services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS), along with advanced capabilities in AI, blockchain, and IoT. It provides a wide range of infrastructure and platform services for building, deploying, and managing applications and services in the cloud.
Key Services: IBM Virtual Servers, IBM Cloud Object Storage, IBM Db2 on Cloud, IBM Watson services, IBM Blockchain Platform.
Alibaba Cloud:

Overview: Alibaba Cloud, also known as Alibaba Cloud Computing or Aliyun, is the cloud computing arm of Alibaba Group, one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies. Launched in 2009, Alibaba Cloud offers a comprehensive suite of cloud services to support businesses and organizations in various industries.
Key Services: Elastic Compute Service (ECS), Object Storage Service (OSS), ApsaraDB for RDS, Alibaba Cloud AI services, Alibaba Cloud CDN.
Oracle Cloud:

Overview: Oracle Cloud is the cloud computing service offered by Oracle Corporation, one of the world’s largest providers of enterprise software and hardware solutions. Oracle Cloud provides a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including infrastructure, platform, and software services, designed to support businesses in their digital transformation journey.
Key Services: Oracle Compute, Oracle Cloud Storage, Oracle Autonomous Database, Oracle Cloud Functions, Oracle AI services.
Red Hat Hybrid Cloud:

Overview: Red Hat Hybrid Cloud combines the flexibility and scalability of cloud computing with the security and control of on-premises infrastructure. It offers businesses the ability to seamlessly integrate their existing systems with cloud services, enabling them to build, deploy, and manage applications across hybrid environments. With Red Hat Hybrid Cloud, organizations can optimize their IT resources and accelerate innovation while maintaining data sovereignty and compliance.
Key Services: Red Hat OpenShift, Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Red Hat Satellite, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes.
What is Hybrid Cloud? Explain
A Hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines elements of both public cloud and private cloud. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both cloud models, providing greater flexibility and scalability.
Easy way: A Hybrid Cloud is like having two types of cloud computing merged together: one that’s private and controlled just by your organization, and another that’s public and accessible over the internet. It’s like having the best of both worlds. With this setup, you can keep your sensitive data and applications in the private cloud for security, while using the public cloud for things like accessing apps from anywhere and saving costs. This way, you get flexibility and control over your data and applications, which helps your business adapt and grow more effectively.
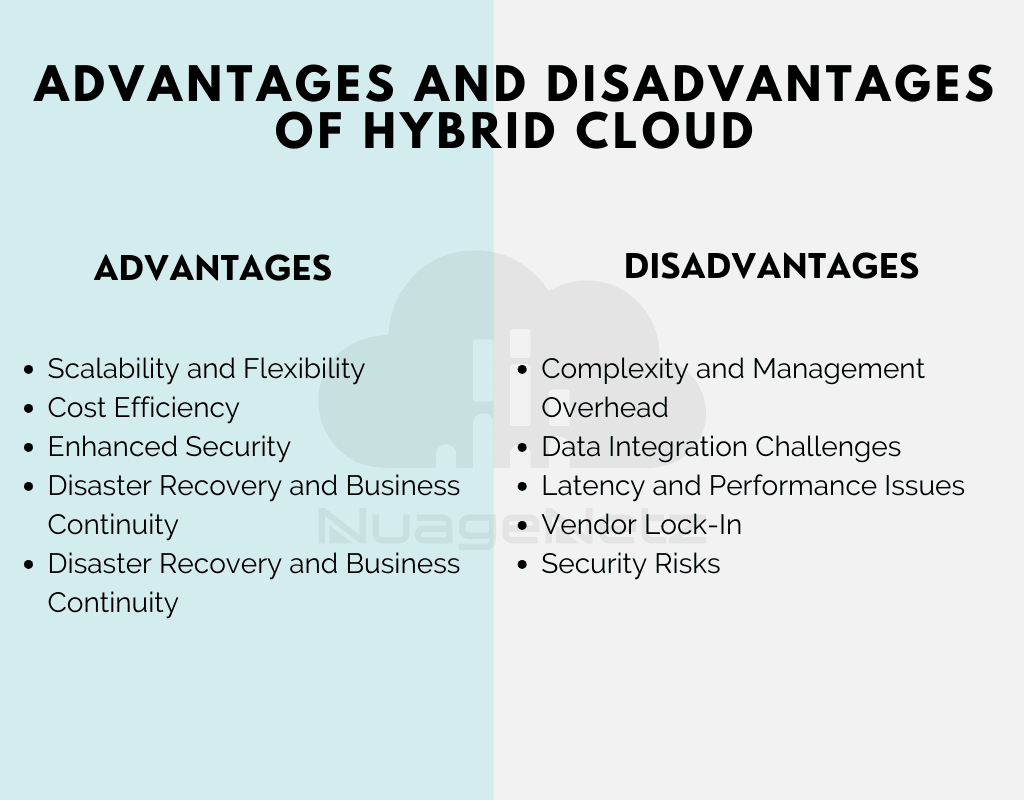
Explore the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid cloud
Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud: Understanding the Differences
Hybrid-Cloud:
- Hybrid cloud refers to a computing environment that combines public cloud resources with private cloud or on-premises infrastructure.
- It allows organizations to leverage the scalability and flexibility of the public cloud for certain workloads while keeping sensitive data or critical applications on-premises or in a private cloud for security or compliance reasons.
- The hybrid cloud model provides a seamless integration between on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services, allowing data and applications to move between them as needed.
Multi-Cloud:
- Multi-cloud refers to a strategy where an organization uses services from multiple public cloud providers, such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or others.
- Unlike hybrid cloud, multi-cloud does not necessarily involve on-premises infrastructure or private clouds. Instead, it focuses on leveraging the strengths of different cloud providers for various workloads or applications.
- Multi-cloud strategies can be driven by factors such as avoiding vendor lock-in, accessing specialized services or features offered by different providers, or distributing workloads across multiple clouds for redundancy and disaster recovery.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations approach IT infrastructure, software delivery, and digital transformation. With its scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency, cloud computing empowers businesses of all sizes to innovate, scale, and compete in today’s fast-paced digital economy.
We’ve discussed the essential concepts of cloud computing, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). We’ve explored the differences between public, private, and hybrid clouds. Moreover, we’ve highlighted some of the most popular cloud service providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
In conclusion, cloud computing is not just a technological trend but a fundamental shift in how businesses operate and innovate in the digital age. By embracing cloud computing, organizations can unlock new opportunities, drive efficiency, and stay ahead of the competition.
About Us
NuageNetz IT Services Pvt. Ltd. is a cutting-edge IT company that specializes in Cloud Computing, Web Development, DevOps and Agile Methodologies. Our team of skilled professionals is dedicated to providing exceptional services to our clients using the latest technologies and tools
Got Something to say about our Blog?
Have something to say? Drop your thoughts, feedback, or questions in the comments below!